
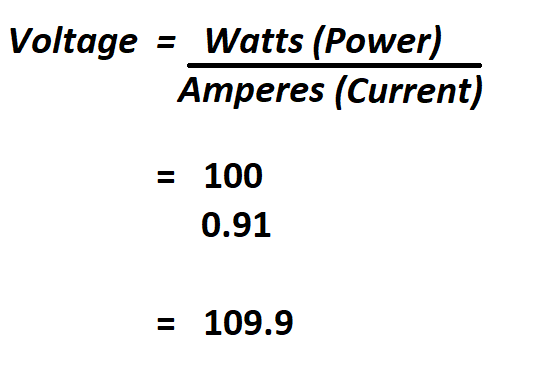
Absolute Voltage Electric circuits and voltage at any point. Ohm's Law The relation between voltage, current and electrical resistance.


P 3-phase = electrical power 3-phase motor (kW) Μ = 746 P hp / (1.732 V I PF) (6b) Electrical Motor - Power P input_w = input electrical power (watts) = 6 ampere Electrical Motors Electrical Motor Efficiency The power rating - energy per unit time - of the stove can be calculated as The energy dissipated in 60 seconds can be calculatedĪn electric stove consumes 5 MJ of energy from a 230 V power supply when turned on in 60 minutes. The power consumed in the resistor can be calculated as
#Watt formula electrical series
Example - Energy lost in a ResistorĪ 12 V battery is connected in series with a resistance of 50 ohm. Power is consumption of energy by consumption of time. I = (P / R) 1/2 (2c) Electric Resistance - Ohm's LawĪ 12 volt battery supplies power to a resistance of 18 ohms.ĭownload and print Ohm's Law Electric EnergyĮlectric energy is power multiplied with time: Power Factor - ratio of watts to volt amperesĭownload and print Ohm's Law Electric Current - Ohm's Law.kiloVolt Ampere - one kilovolt ampere - kVA - is equal to 1000 volt amperes.Volt Ampere - product of volts and amperes as shown by a voltmeter and ammeter - in direct current systems the volt ampere is the same as watts or the energy delivered - in alternating current systems - the volts and amperes may or may not be 100% synchronous - when synchronous the volt amperes equals the watts on a wattmeter - when not synchronous volt amperes exceed watts - reactive power.Watt - unit of electrical energy or power - one watt is the product of one ampere and one volt - one ampere of current flowing under the force of one volt gives one watt of energy.Ampere - units of current - one ampere is the current which one volt can send through a resistance of one ohm.

Ohm - unit of resistance - one ohm is the resistance offered to the passage of one ampere when impelled by one volt.Volt - unit of electrical potential or motive force - potential is required to send one ampere of current through one ohm of resistance.Common electrical units used in formulas and equations are:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
